Exploration and practice of green building - three-dimensional greening
We explore the multi-facade greening system, seek the possibility of "Peak Carbon Dioxide Emissions and Carbon Neutrality" from the three-dimensional space, and empower the green development of buildings. Facade creates a vertical green ecological environment, provides a comfortable and friendly natural environment and creates ecological diversity in the city center.
Three-dimensional greening refers to roof greening, wall greening, structure greening and platform greening. Three-dimensional greening is no longer "making use of every bit of time", but "borrowing land from the air" to improve the landscape green viewing rate and ecological efficiency. In terms of three-dimensional greening technology research and policy making, it started in Germany at the earliest, and then expanded all over the world. The most perfect development is Germany, Japan and Singapore. At the end of 2003, the total roof greening area in Germany was close to 100 million square meters, and by 2007, the roof greening rate in Germany was up to 80%.
01 Explore the development of three-dimensional greening in Germany
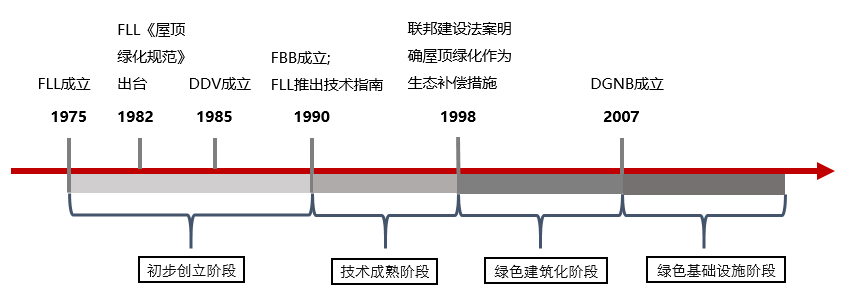
Notes:
FLL:German Society for Landscape Research, Development and Architecture
DDV:German Roof Garden Association
FBB:German Green Building Professional Association
DGNB:German Council for Sustainable Building
Initial foundation stage: 1975-1990 (technical public relations based on environmental and ecological considerations). In 1990, after accumulating more experience, FLL issued a more perfect Guide to Design, Installation and Post-maintenance of Green Roof, which marked the comprehensive maturity of Germany in the technical fields of plant configuration, roof construction technology, process, materials and construction. In the same year, an independent team from FLL Association established the German Green Building Professional Association (FBB).
Technical maturity stage: 1991-1997 (complete technical system and mature laws and regulations). During the period, the German federal government and state governments successively issued laws and regulations related to three-dimensional greening; During the period, new technologies were studied, such as new technologies of roof construction, quantitative research on rainwater management and water seepage capacity, and research on solar energy utilization of roof garden; In the society, from "construction" to "use", the discussion on the achievements and benefits of roof greening construction is increasing day by day.
Green building stage: 1998-2007 (green building efficiency is the leading factor). In 1998, the Federal Construction Law defined roof greening as an ecological compensation measure and source control means, and stipulated roof greening as the most basic requirement in land use planning. The relevant laws and incentive policies have improved the supporting norms and policies around this major change in regulation. During the period, the cross-study of different disciplines is an important trend, and the extension of research scope expands rapidly. Rainwater management research is a key field, including rainwater treatment, infiltration and filtration, water storage tank design, rainwater retention, and rainwater flood mitigation.
Green infrastructure stage: 2008 - present (green infrastructure for climate change). In 2007, the Deutsche Gütesiegel für Nachhaltiges Bauen (DGNB) was established, which marked the formal formulation of a national green building evaluation system. During the period, the research on the technical level mainly focused on the integration technology of solar energy and three-dimensional greening; Germany has studied the efficiency of climate regulation of urban microenvironment with three-dimensional greening; In terms of rainwater management, there is also a cross-disciplinary academic trend, which is gradually brought into the emerging research category of urban green infrastructure.
02 Explore the Development of Three-dimensional Greening in Singapore
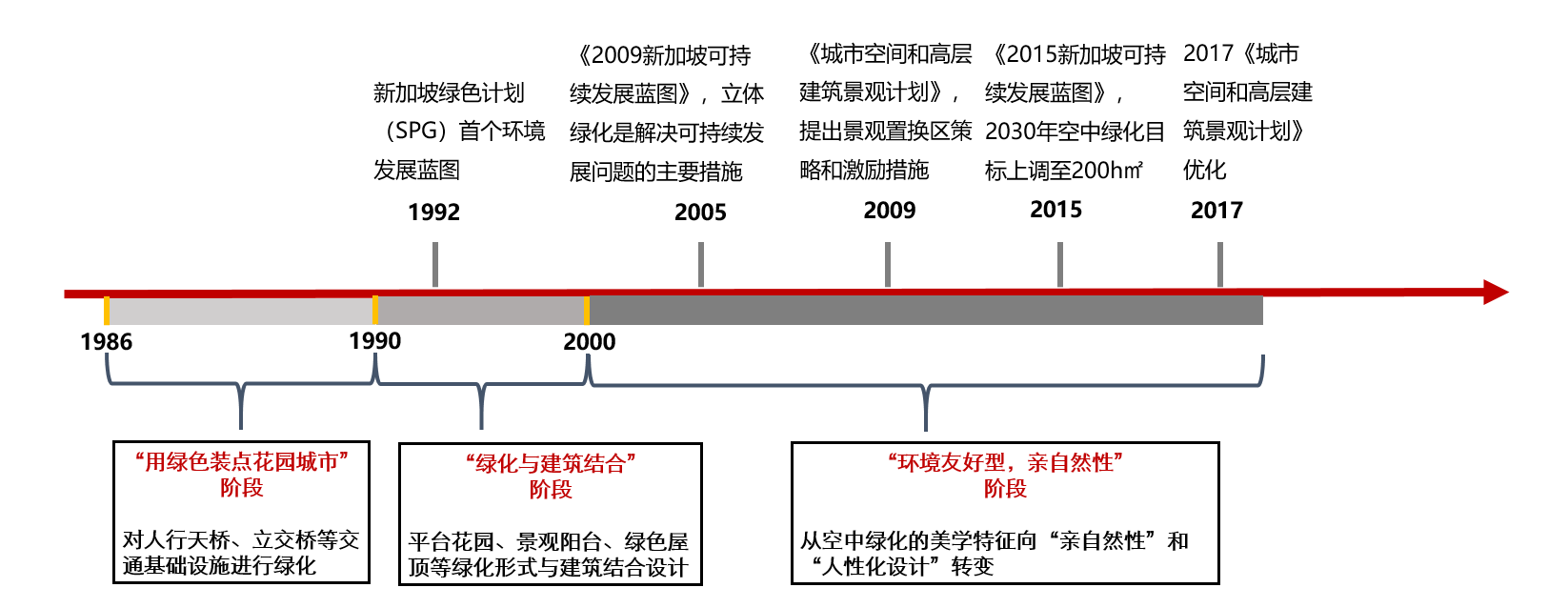
The development of three-dimensional greening in Singapore is divided into the following three stages, from the initial bridge greening, to the combination with architecture, and then to the innovative three-dimensional greening based on people. The forms and connotations of three-dimensional greening in Singapore are gradually enriched.
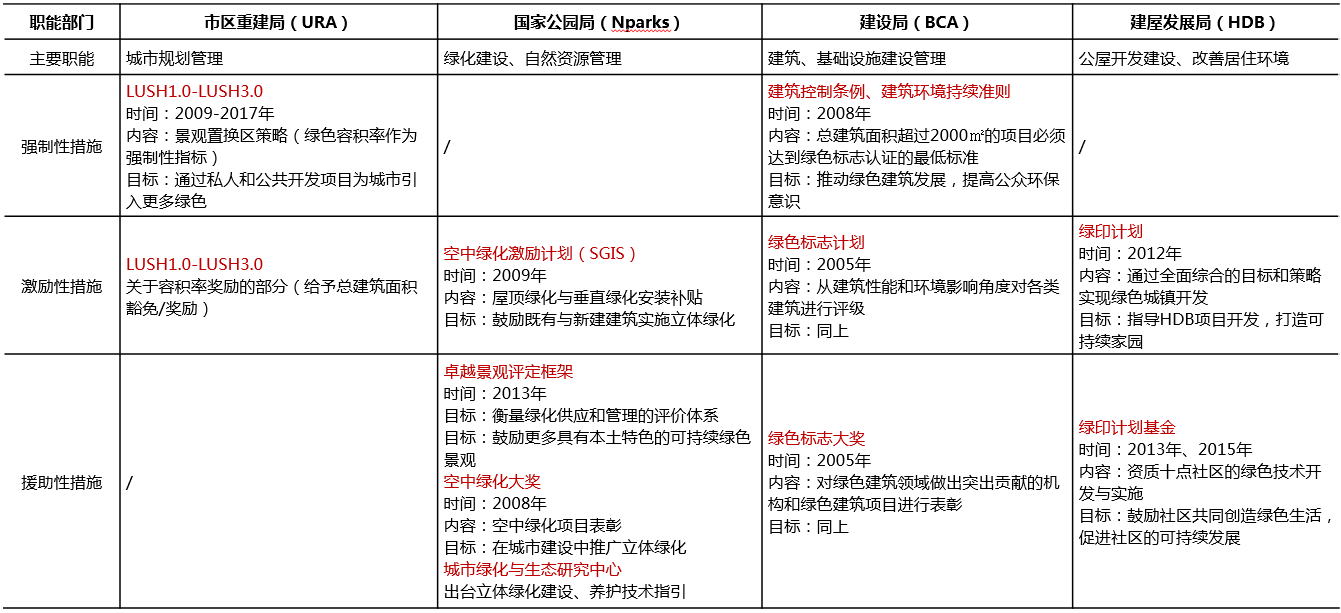
Control and guidance of three-dimensional greening in Singapore:
1)Planning control (mandatory measures)
In 2009, the Urban Space and High-rise Building Landscape Plan (LUSH1.0-3.0 Plan) was released, and the Singapore Sustainable Development Blueprint was released in 2015. The goal is that the total area of air greening in China will be 200h㎡ in 2030. As of July 2018, the existing air greening area in Singapore has been up to 100h㎡. The planning and control process of green space greening in Singapore: Conceptual planning and master planning - development guidance planning - building control (detailed control requirements for the form and area of three-dimensional greening are made at the micro level).
2)Policy guidance (guiding policy)
Incentive measures: Included in the urban green space area, floor area ratio reward, financial subsidies, and included in the green building scoring system.
Aid measures: Three-dimensional greening technology and financial support, recognition and reward, publicity and promotion are supplements to mandatory and incentive measures.
Three-dimensional greening technology in Singapore
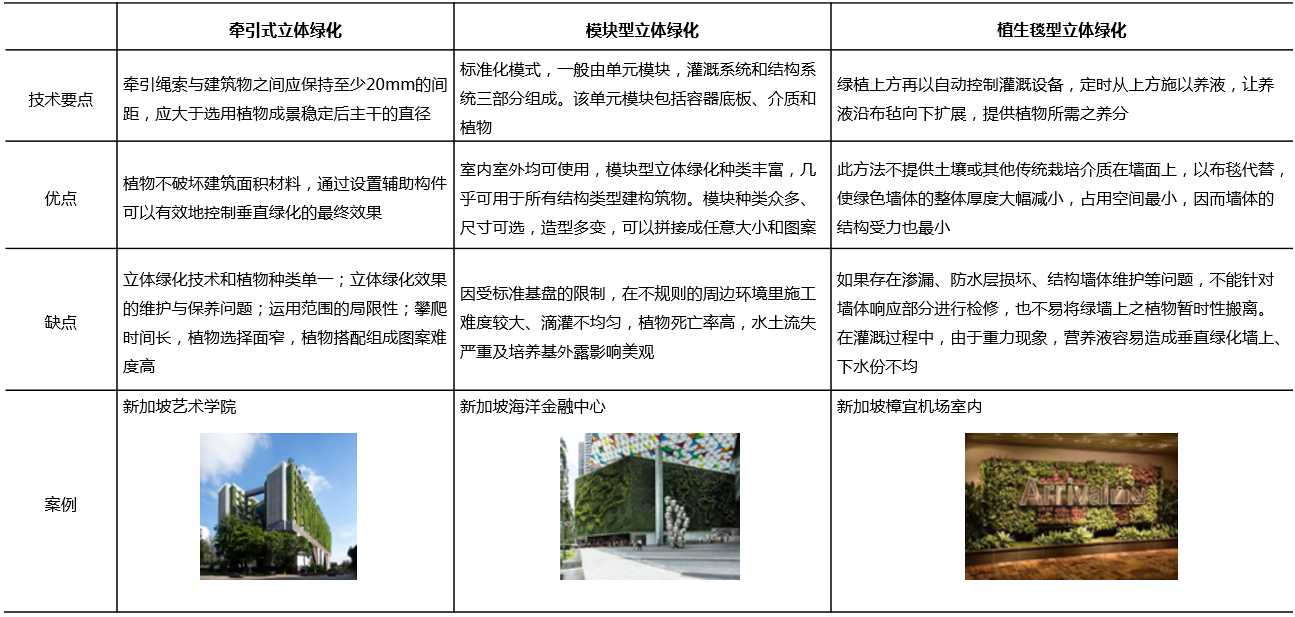
03 Exploration Path of Three-dimensional Greening Development in China:
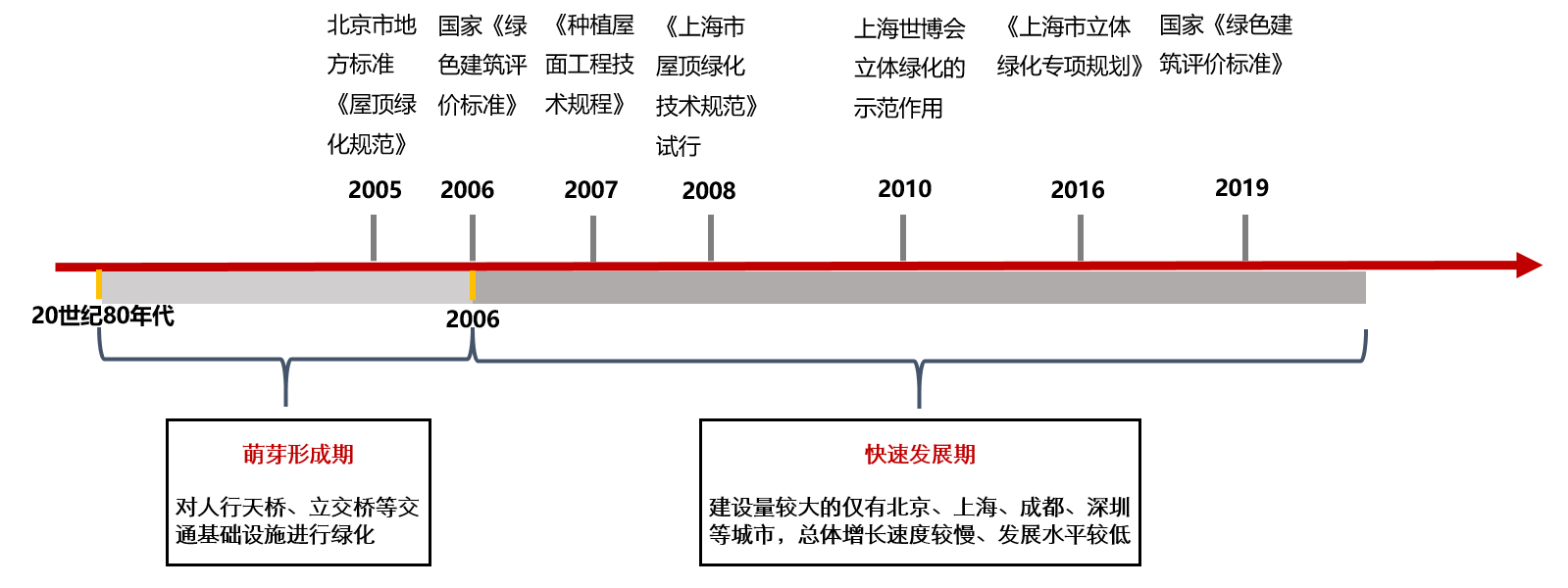
04 Thoughts on the future of three-dimensional greening in China
Legalization - Improve the legal system and promote the normalization and effective connection of three-dimensional greening construction;
Systematization - Incorporate three-dimensional greening into assessment indicators, improve quantitative evaluation indicators of urban greening, and increase reporting procedures;
Standardization - Formulate unified standards and evaluation and reward mechanisms;
Characterization - Combine regional characteristics and development status, solving specific urban problems and increasing incentive policy types;
Benefit - Improve efficiency and pursue of comprehensive benefits of ecology, economy and society; Informatization - Build a network platform, emphasize public participation and information transparency.
Informatization - Build a network platform, emphasizing public participation and information transparency.