1.Foreword
Stone is one of the building decoration materials with a long history, and it is also the decoration material that many architects and developers prefer to use. Natural stone is a kind of microporous material. There are tiny gaps between stone crystals, which we call micropores. Stone has natural permeability because of its micropores. The size of micropores in different textures of stone is different, and the permeability of stone is usually determined by the size of these micropores. It is very important to keep the natural permeability of stone. Only by keeping the pores of stone unblocked, the moisture at the bottom of stone will volatilize, and there will be fewer chances for stone to have problems in humid environment. It is also the capillary action produced by these micropores of stone that makes stone have different water absorption rates. If the stone is not well protected before installation, there will be water spots, dirt spots, white spots (saltpetering), rust spots and other phenomena in the use process, which will affect the decorative effect and service life of the stone.
The harm of rainwater, especially acid rain, to stone is mainly reflected in the facades of buildings. We often see the water stains on the stone walls of some buildings, which are caused by the alkaline precipitation and moisture absorption caused by the infiltration of rainwater into the walls. The yellow embroidery spot on the light-colored stone is the product of further oxidation and diffusion of the oxide in the stone under the action of water.
In addition, a lot of pollution is also formed by the infiltration of dirt with water as the carrier into the stone. In winter, the freeze-thaw phenomenon caused by the infiltration of rainwater or snow water also causes great damage to the stone. It is natural for stone to absorb water, and it is inevitable for stone to encounter water. Therefore, what we need to do is to prevent and reduce the harm of water to stone.
From the above, we usually require stone protection in the design and construction of the stone curtain wall in order to ensure the durability of the stone curtain wall. The protection of stone is to prevent water and pollution. The material used is a liquid specially used to protect stone-stone protective agent. Its function is to effectively reduce the water absorption of stone and improve the anti-pollution ability of stone.
According to the definition in the Natural Stone Protective Agent for Architectural Decoration (JC/T 973-2005), the stone protective agent is a solution that can prevent natural stone from producing white spots, water spots, rust spots and other pathological changes, effectively reduce the water absorption of stone, and improve the stain resistance and corrosion resistance of stone. The main components of the stone protective agent can be organically combined with natural stones, the appearance of the stones is not obviously changed, the water absorption of the stones is effectively reduced, the anti-fouling performance of the stone is obviously improved, and the effect is relatively stable under acid and alkali conditions.
From the above definition, it can be seen that the function of stone protective agent is to effectively reduce the water absorption of stone and significantly improve the anti-pollution ability of stone. The functional indicators of these two products are of great significance for maintaining and reflecting the decorative effect of stone for a long time, preventing pathological changes and weathering, and reducing the complicated daily maintenance workload.
The protection of stone is to adopt the methods of brushing, spraying, rolling, drenching and soaking to make the protective agent evenly distributed on the surface of stone or penetrate into the stone to form a kind of protection, so that the stone has the functions of waterproof, anti-fouling, acid and alkali resistance, anti-aging, anti-freezing and thawing, anti-biological erosion and so on, so as to achieve the effect of improving the service life and decorative performance of stone.
Stone protective agent is mainly composed of solute (active ingredient), solvent (diluent) and a small amount of additives. Different stone protective agents have different construction requirements. Before construction, a feasible construction scheme should be formulated according to the instructions for use of the protective agent and the actual situation of the site.
2. Classification of stone protective agents
1. According to the type of solvent:
Aqueous type: It is to have the material of protective property to use water to serve as dilute medium and blend.
Solvent type: It is to use special solvent as dilution medium to blend substances with protective properties.
Aqueous protectants generally have less odor, low toxicity, no combustion and high safety performance. Solvent-based protective agents generally have strong odor, relatively high toxicity, flammability, and density generally less than 1. Solvent-based solvents are divided into inorganic solvents and organic solvents. The solvents we usually use are organic solvents, which can be divided into 10 categories according to their chemical structures:
Aromatic hydrocarbons: benzene, toluene, xylene, etc.;
Aliphatic hydrocarbons: pentane, hexane, octane, etc.;
Alicyclic hydrocarbons: cyclohexane, cyclohexanone, toluene cyclohexanone, etc.;
Halogenate hydrocarbons: chlorobenzene, dichlorobenzene, dichloromethane, etc.;
Alcohols: methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, etc;
Ethers: diethyl ether, propylene oxide, etc.;
Esters: methyl acetate, ethyl acetate, propyl acetate, etc.;
Ketones: acetone, methyl butanone, methyl isobutyl ketone, etc.;
Diol derivatives: ethylene glycol monomethyl ether, ethylene glycol monoethyl ether, ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, etc.;
Others: acetonitrile, pyridine, phenol, etc.
The determination of toxic substance limit of solvent-based protective agent shall be in accordance with the Indoor Decorating and Refurbishing Materials-Limit of Harmful Substances of Solvent-based Wood Coatings GB 18581-2009, and the content of toxic substance shall be controlled within the limit of national standard.
2. According to the functional classification, it can be divided into:
Waterproof (FS): A protective agent that prevents water and water-based contaminants from penetrating into the stone.
Oil-proof type (FY): It is a protective agent that can prevent oil and oily pollutants from penetrating into stone, and has the basic function of waterproof type.
3. It can be divided into the following according to the use of parts :
Finish type (SM): protective agent for dry-hanging stone (six sides) and wet-pasting stone decorative surface (including four sides).
Bottom surface type (DM): used as the protective agent for the back (bottom surface) of the stone when the ground stone is wet pasted and the wall stone is grouted.
4. According to the type of protective layer, it can be divided into:
Penetration type: all the active ingredients go deep into the pores of the stone and react to produce a protective layer. Generally, there is no residue on the surface, which will not affect the decorative effect of the surface.
Sealed type: The active ingredients form a film on the surface of the stone, and the traces of the resin coating can be clearly seen on the surface, which completely or slightly changes the decorative effect of the stone surface. Uch as a stone reducing agent, a stone sealing agent, a mercerizing sealing agent and the like.
5. Classification by solute composition
Acrylic protective agent: a protective agent with acrylic resin as the main active ingredient (solute). With sealing performance, it will form a film after being applied on the surface of stone, with plastic light, but the aging resistance is not enough, and the color of stone will be deepened after being applied. It is suitable for protective treatment of rough stone surface or stone bottom which needs to be sealed. It belongs to the second generation protective product (the first generation is wax).
Silicone-C protective agent: a protective agent with the compound of acrylic resin and silicone as the main active ingredient (solute). This product is a transitional product from acrylic protective agent to organosilicon protective agent, which solves the shortcomings of easy yellowing and short life of acrylic acid. It is the second generation of improved products.
Organosilicon protective agent: a protective agent with organosilicon as the main active ingredient (solute). Commonly used organic silicon is methyl sodium silicate, methyl silicate, silane, siloxane, etc. This kind of protective agent is characterized by the chain of organic silicon in a network structure, strong permeability, and breathability, does not change the color of stone. Its disadvantage is that it has poor oil resistance and is suitable for any surface treatment of all stones. Organic silicon stone curing agent is the main product type in the market at present, which belongs to the third generation product.
Silicon fluoride type: a protective agent with the compound of organic silicon and fluorine as the main active ingredient (solute). This product inherits the advantages of silicone and enhances the anti-oil, anti-fouling and anti-aging properties, which is the best protective product at present. It is suitable for any surface treatment of all stones with special protection requirements, and belongs to the fourth generation of products.
At present, there are many kinds of protective agents sold in the Chinese market, including domestic and imported ones. When selecting protective agents, it is necessary to consider whether the selected protective agents are harmful to the environment, operators and users. The selected stone protective agent should have corresponding product instructions and complete and effective inspection reports from national authoritative inspection agencies, and the products should meet the national quality standards.
Table 1 Evaluation Standard of Stone protective agent
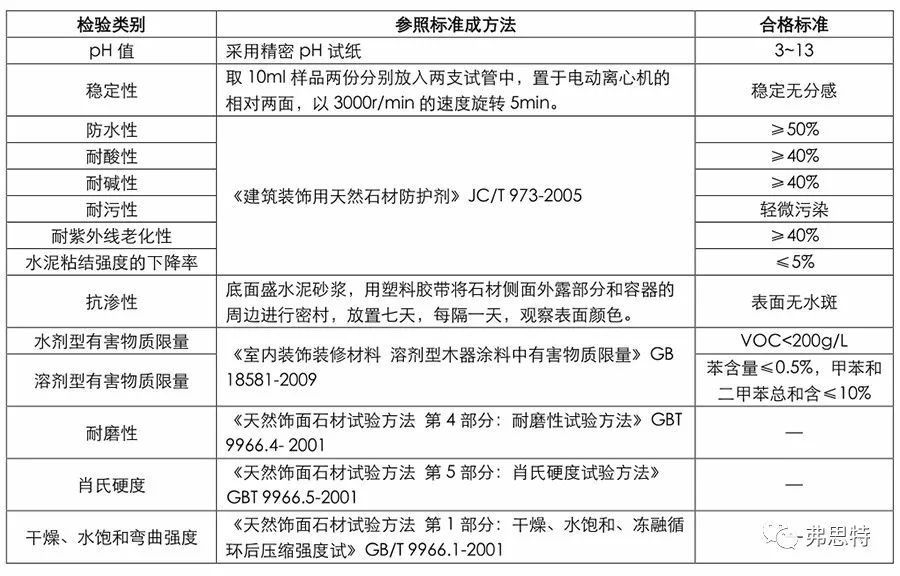
The Natural Stone Protective Agent for Building Decoration (JC/T973-2005) is currently the only quality standard for protective agents in China.
3. Common diseases of stone
1. Efflorescence: A white or off-white mist substance generated on the surface of stone, which affects the beauty of stone, commonly known as saltpetering.
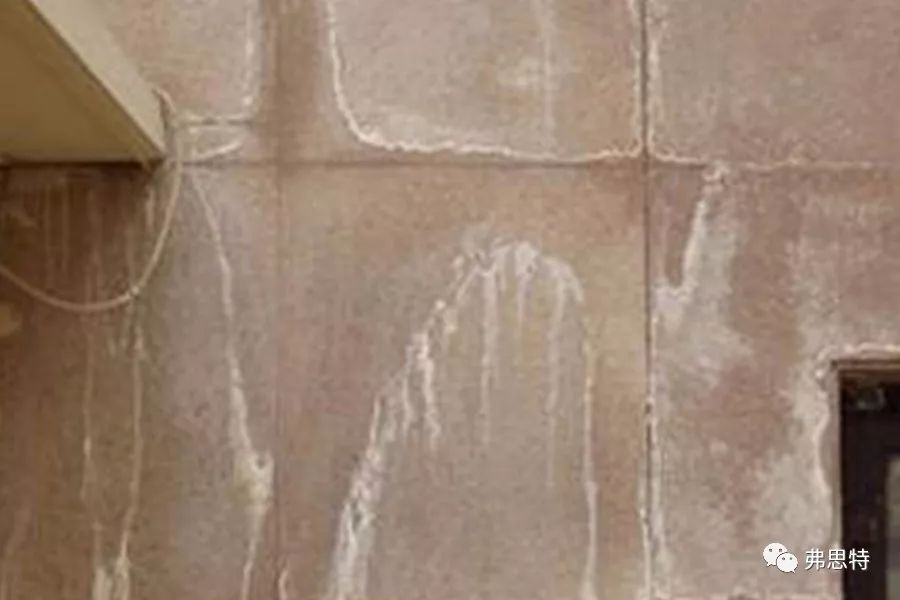

▲ Efflorescence (saltpetering) of stone
There are two reasons for efflorescence. One is that during wet paste construction, the cement mortar produces chemical changes to form calcium hydroxide, which comes out from the joints of the stone or the grain of the stone itself and combines with carbon dioxide in the air to form white crystals; the other is that rainwater seeps into the stone interior and contacts with the cement mortar to produce chemical changes and form efflorescence.
2. Water spot: After the stone installation is completed, it will not dry for a long time and always leave wet traces on the surface, which is commonly known as water spot.
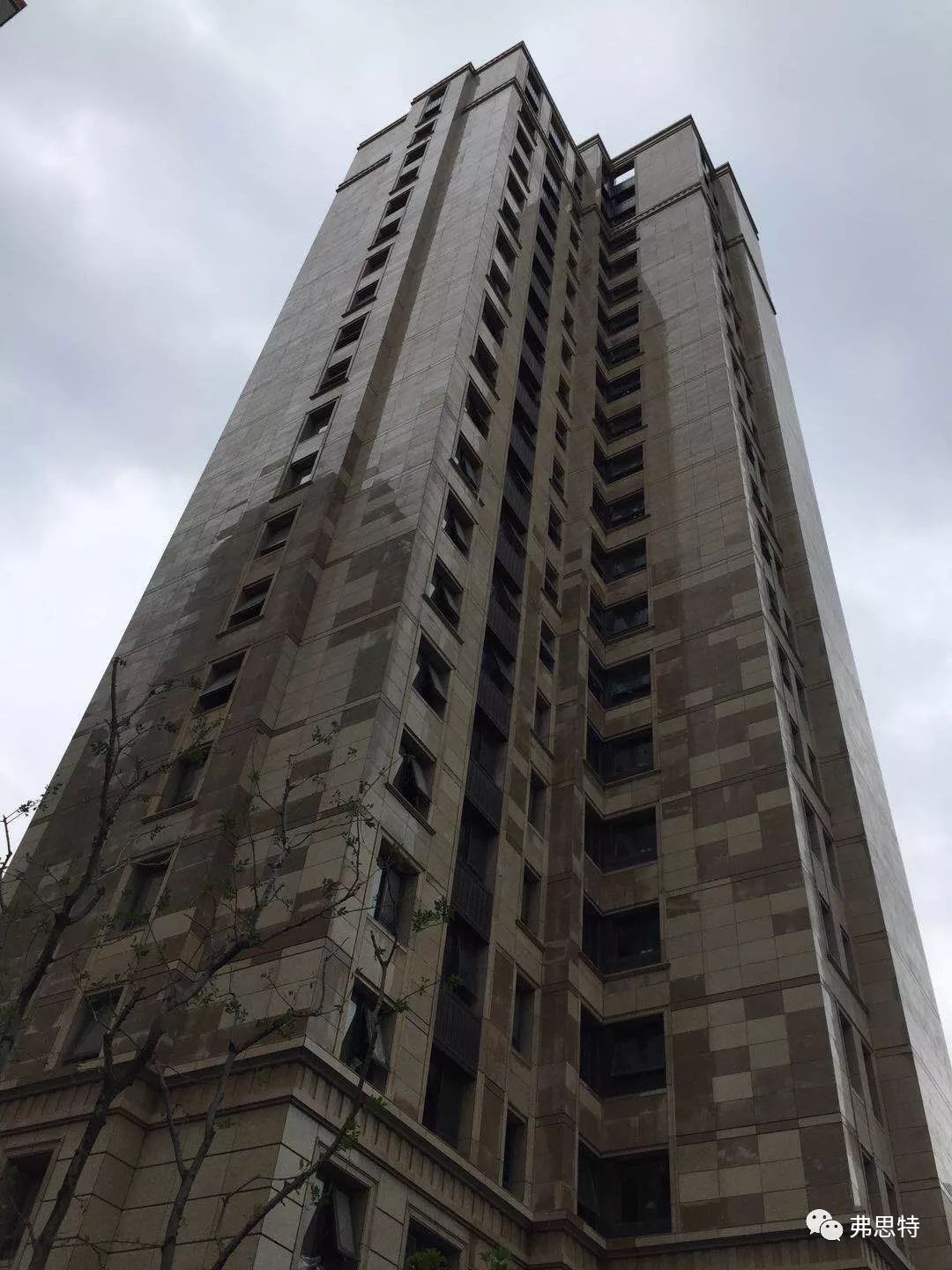

▲ Water spot of stone
The formation of water spots is very complex, including cement, acid rain, saltpetering, poor sand quality and underground pollution.
3. Rust spot: The cause of rust spot generally comes from the iron contained in the stone itself. When rainwater comes into contact with the iron in the stone, it slowly forms rust and produces rust spots. This kind of rust is not easy to remove, the most important thing is to prevent water from infiltrating into the stone to prevent the formation of rust.
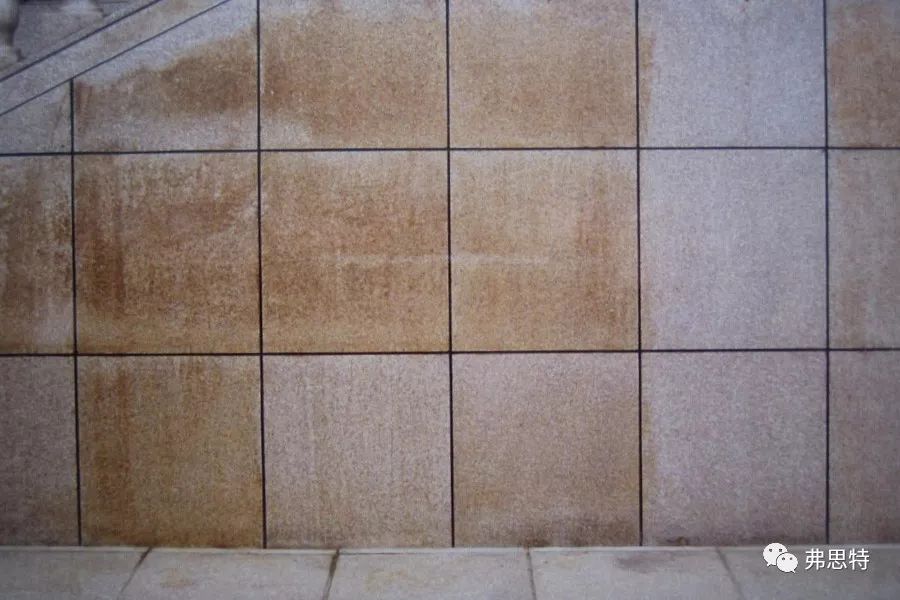

▲ Rusty spot of stone
4. Freeze and thaw. Natural stone freezing and thawing phenomenon mainly occurs in the north and other places where the weather is relatively cold. When the pores of the stone absorb enough water, once the temperature drops below 0 C, the water in the stone begins to freeze and the volume expands. When the expansion force of the ice is greater than the structural force of the stone, the stone will break.
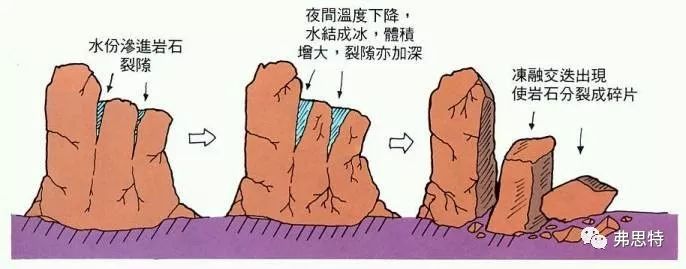

▲ Freezing and thawing of stone
Because the main factor of stone freezing and thawing is water, we can prevent the occurrence of stone freezing and thawing as long as we prevent water from entering natural stone.
4. Stone protection
In the early days, people thought that wax was the best protective agent, which could prevent water infiltration and material contamination. But after waxing the stone surface, although the external water and moisture can not enter the stone interior, but the moisture inside the stone can not be emitted, moisture accumulated inside the stone, will also lead to stone lesions. At the same time, with the increase of waxing times, the color of stone will deepen, and wax is easy to be polluted, such as silt and dust will be embedded in wax, forming wax scale, which is very inconvenient to clean, so frequent waxing will also damage the surface of stone and shorten the life of stone.
The protective principle of the stone protective agent is to make the effective substances go deep into the stone with the solvent. After the solvent volatilizes naturally, the effective substances remain inside and on the surface of the stone, forming a breathable but impermeable protective barrier to prevent external pollution and water infiltration. It does not affect the appearance of the stone, but also maintains the "breathing" of the stone, so that the moisture in the stone will not stay in the stone and cause the pathological changes of the stone. After protective treatment, the stone not only has strong anti-pollution ability, but also is very convenient to clean. Because dust and dirt only stay on the surface of the stone and will not penetrate into the stone, they can be removed with clean water or daily cleaning liquid to restore the original brightness of the stone. At the same time, after treatment, the stone can enhance its strength and hardness, improve its wear resistance, resist aging and prolong its life.
1. Selection of protective agent
According to the type of stone used in the project, the correct selection of stone protective agent is one of the key factors to ensure the quality of stone maintenance project. Each stone protective agent is not omnipotent, and its performance is mainly manifested in universal applicability, that is, it is effective for most stones. But on the other hand, each kind of stone also has its particularity, that is, one kind of protective agent is particularly good for some stones, while another kind of stone is not ideal or even ineffective. Based on this, when we choose the stone protective agent, we must make the right choice according to different stone varieties, different environments, different installation processes and different protection requirements.
The selection of protective agent should be based on the purpose of stone protection. Attention should be paid to the adaptation of stone varieties, natural attributes, structure and processing technology, as well as the use environment of stone.
1.1 The stone is required to have strong ultraviolet resistance, water resistance and acid resistance to prevent stone saltpetering and rust spots. Generally, organic silicon stone protective agent is used.
1.2 To prevent light-colored stone (such as Yashi white, jazz white, white marble, etc.) from rusting or to prevent silicone weather-resistant adhesive oily substances (plasticizers) from penetrating into the side after caulking, resulting in dark shadows at the edges of stone crevices, oil-proof interface protective agents can be selected.
1.3 The purpose of protection is to integrate waterproof and anti-fouling capabilities. Generally, organic fluorine type stone protective agent can achieve the effect.
1.4 If the bottom of the building is installed by wet pasting process, it is recommended to use the special curing agent for the bottom of the stone to protect the bottom and the four sides. The selection of bottom curing agent should pay attention to the alkali resistance of curing agent, and can not affect the bonding fastness of stone and cement.
In short, it is to adhere to the four "specific" principles when choosing the stone protective agent: according to the specific stone, the specific installation method, the specific pollution source to be prevented, and the selection of the specific stone protective agent.
First of all, the protection of stone should be waterproof, because water is the carrier of many pollutants, and the waterproof of stone protective agent should be combined with the acid resistance and alkali resistance of stone protective agent to analyze and judge meaningfully, it is incorrect and one-sided to judge the quality of stone protectant only by the waterproof index. The higher the waterproof index of the stone protective agent, the same or close to the acid and alkali resistance index, the better the stability of the protective agent, and the longer the effect will be maintained in the acid and alkali environment.
2. Construction process of stone protective agent
The construction of stone protective agent usually adopts two methods: brushing method and spraying method.
Brush coating method: Brush coating method is to use brush, roller, sponge and fadeless cloth to coat the protective agent on the stone surface.
Spraying method: The tools used in spraying method include sprayer, spray gun and air compressor.
Before use, carefully read the instructions for use of the selected waterproofing agent, operation methods and matters needing attention during operation.
2.1 Cleaning. The stone to be coated with stone protective agent must be clean and should be cleaned with special cleaning agent for stone. Because the stains on the stone surface will be brought into the stone and solidified in the micropores of the stone in the process of brushing the protective agent, forming marks that are difficult to remove, the rust, oil and dust on the stone surface should be cleaned up before brushing the protective agent, preferably immediately after cutting, and dried for use.
2.2 Drying. Before painting the stone protective agent, the stone board should be dry, and the moisture content should not be higher than the relevant national standards. The purpose of making the stone dry thoroughly is to make the stone fully absorb the protective agent so as to achieve the ideal protective effect. In the season of low temperature and high relative humidity, it is recommended to use the drying room to dry the slate, and use the gas spray gun to dry the slate with caution.
Attention shall be paid to the following items when drying the slate:
2.2.1 Drying room. In the northern winter, the construction of drying room can improve the indoor temperature, effectively accelerate the drying speed of stone, and ensure the quality of protective agent painting, so it is suitable for large-scale projects. However, ventilation, fire prevention and gas poisoning prevention should be strengthened in the drying room.
2.1.2 Gas spray gun. Gas spray gun can be used for local drying of stone, but the moving speed of the gas spray gun on the stone slab should be well controlled. If the speed is too fast, the temperature of the stone surface is not high enough to effectively remove the water in the stone gap; if the gas spray gun moves too slowly and concentrates at a certain point, the heat conducted to the stone surface will be too much, resulting in local temperature is too high, and in serious cases, it will cause local expansion and cracking of the stone surface. The method is convenient and quick, and is suitable for the drying of local parts and corners, such as the condition that the protected stone is wetted when being cut again. Generally, the gas spray gun should not be used in large area drying of stone. The use of gas spray gun should also strengthen the ventilation, fire prevention and gas poisoning prevention of the construction site.
Whether the stone is dried in the factory or on the construction site, the temperature of the stone should be reduced to below 40℃ after heating before the protective agent can be applied. Because the temperature is too high, the protective agent is dried before it completely penetrates into the stone, the penetration effect is not good, and after the first hardening, the second brushing is difficult to penetrate deeply, and ultimately the protective effect is reduced. For solvent-based protective agents, the temperature should not be too high.
3. Application and dosage of protective agent
The protective agent must be used in sufficient quantity and evenly. The use of protective agent must be sufficient, if the amount of protective agent absorbed by stone is not enough, it will not produce the desired protective effect. The amount of protective agent used in stone with different density will be different, and the number of times or methods of painting will be different. Such as white sand beige, singed granite, white granite, etc., this kind of stone has a large gap, requiring a larger amount of protective agent to be used, and the number of times of painting should be more than two times (two times of horizontal and vertical painting is one time). A small, single-pass application of the protective agent is generally not sufficient to block capillarity and prevent contamination. For some stones with high density and no high temperature processing cracks, the amount of protective agent used can be relatively small.
For some special stones, such as cave stone and sandstone, the soaking method should be used as far as possible. Immersion method can not completely soak the whole stone in the solvent when making six-sided protection of stone, which will produce hydraulic pressure around the stone, so that the air inside the stone can not be discharged, affecting the penetration of protective agent into the deep interior of the stone, affecting the protective effect of the stone. When soaking, always ensure that the stone has a surface exposed outside the protective agent, so that the air inside the stone can be discharged again. After one side of the stone is treated, turn it over and soak the other side, so as to ensure that the protective agent can better penetrate into the inner layer of the stone and play a role of deep protection.
4. Cleaning
Excess protectant should be removed. Clean cloth shall be used to wipe off the protective agent left on the stone surface during construction. If the stone protective agent is not completely absorbed by the stone and the residual protective agent is not removed, it will leave traces of the protective agent on the surface of the stone after curing, and even cause spots, which are very difficult to remove. The residue of methyl silicate water-based protective agent on the surface of stone will also reduce the glossiness of the surface of stone.
5. Quiet time
It is an important step to ensure the penetration and solidification of the protective agent and the formation of protective function. The rest time is related to the humidity and temperature of the environment at that time. The standing time shall be at least as long as the applied protective agent does not flow when the stone is erected. It can be tested with napkins, and it is better to stick the napkins without sticking and wetting.
6. Curing time
The stone coated with protective agent should be fully maintained overhead, which is an important link in the construction of stone protection. The so-called health preservation is to let the stone coated with protective agent dry naturally under the condition of ventilation, and basically complete the process of chemical change. Generally speaking, it takes 48 hours or more for the water-based protectant to basically complete the chemical change process; the time for the solvent-based protectant to complete the crosslinking and curing process is shorter, but it also takes more than 24 hours. The lower the temperature, the longer the curing time should be. Do not contact water and other pollutants during the curing period.
If the curing time is not enough, it will be installed in a hurry, because the stone protective agent has not been fully cross-linked and cured, acid rain, soluble salts and various soluble pollutants may seep into the stone surface, resulting in a series of pathological changes such as water spots, alkali return, yellowing and rust return, leading to the failure of protection.
The protective effect of any stone protective agent is relative, so the selection of products should be based on the actual requirements and effects, correct construction, and strengthen the later maintenance, in order to achieve the best results.
5. Environmentally-friendly nano protective agent
The environment-friendly nano stone multifunctional protective agent is a newly developed stone protective agent. Nanometer protective agent is a water-based and environmentally friendly stone treatment agent, which is made of nanometer materials and specially treated by nanotechnology. It is non-toxic and harmless to human body.
The protective mechanism of the product is as follows: water is used as a carrier, the main nano active ingredients of the product can penetrate into the interior of a microporous stone and can repair natural fine holes and cracks of the stone, and the nano materials penetrating into the interior of the stone can form a firm whole with minerals such as silicate, carbonate and the like in a stone matrix; and meanwhile, due to the nano effect, Compared with the traditional stone, the stone treated by the nano-stone multifunctional protective agent shows many excellent properties, such as high strength, high wear resistance, self-cleaning, anti-fouling, anti-weathering (anti-oxidation, acid and alkali resistance), antibacterial, and various stone lesions. The stone treated by the protective agent still keeps the air permeability and the natural surface decoration effect.
6. Epilogue
Natural stone contains a variety of natural chemical substances, under certain conditions, the chemical properties of these natural substances may be activated to produce decomposition, or chemical changes occur to damage the surface of the stone, greatly affecting the decorative effect of the stone. In addition, the stone is also very vulnerable to external pollution, if its surface is not properly protected, the external dirt is very easy to invade the external surface and interior of the stone and make the stone ugly, thus greatly reducing the ornamental value and decorative effect of the stone. Therefore, it is very necessary to use high-quality protective agent to protect the surface of stone.